While fun and fulfilling, outdoor gardening can be quite inconvenient because it’s at the mercy of the weather.
A greenhouse is a controllable microclimate that enables you to grow a variety of crops regardless of the weather outside.
To enjoy gardening to the max, read our in-depth guide on how to buy a greenhouse in 2021. You’ll also find a few insider tips and tricks you don’t want to miss so let’s get started.
10 Things to Consider When Buying a Greenhouse

There’s one common mistake all newbie greenhouse owners make. They pick and choose any type of plant that piques their interest. There’s no denying this eclectic selection will look fun and exciting in the beginning. Yet, they’ll ultimately wilt and die.
So, what to do? Well, the best thing you can start with is to decide what type of microclimate you’ll be able to provide for your plants. Then, choose the types of plants most suited for that environment.
Having some basic knowledge of plant needs can go a long way. Some plants need warm nights, others prefer the cold. Some need bright lights, whereas others like filtered shade.
You’ll either need to consider the plants to add based on the the greenhouse you have or choose a greenhouse based on the type of plants you want to grow in it. Regardless of which option works for you, the tips for how to buy a greenhouse in 2021 are the same.
Assembly
Before buying a greenhouse, the first thing you need to do is take a look at the assembly requirements. Greenhouses are typically sold as kits. They’re shipped as flat panels that you’ll need to assemble.
- Learn about 4×8 greenhouse kits
- Learn about 8×16 greenhouse kits
Most greenhouse kits take anywhere from 4 to 5 hours to put together. Yet, it’s better to be on the safe side and set aside a weekend to get it done. Just make sure you brush up on a few simple and basic handyman skills before getting started.
It’s worth mentioning that there are custom-design greenhouses available. Yet, these tend to be more costly.
Permits

After figuring out the assembly, the next step is to check your local zoning regulations. Some areas have restrictions on setup requirements or sizes.
Other areas might require permission or zoning permits before installation. Check out this guide on the subject of greenhouse permits before breaking ground otherwise you may run into problems with the law.
Sizing
The most common sizes are 6×8 feet or 8×10 feet. Even though they’re referred to as ‘small,’ these are still able to provide plenty of room for your plants.
They usually have a central path with border soil on one side for short plants. Then, the opposite wall has all the shelves and tall plants.
Greenhouse suppliers recommend you buy one size larger than you originally planned. You can run out of space quickly once your greenhouse is full.
Location
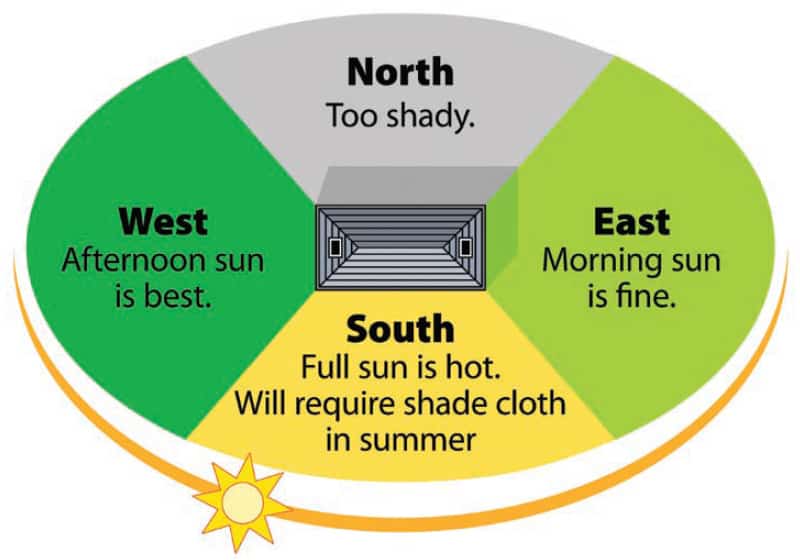
To make the most out of your greenhouse, you have to choose the best location. Experts recommend finding a spot that gets anywhere from 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day.
Also, try to find somewhere as near to your home as possible. It’ll make things easier on you, as well as provide your home with a little extra heat under the colder months.
Frames
Framing gives your greenhouse its structural integrity. It also provides an aesthetically-pleasing addition to your home.
Try to find panels that offer a smooth and continuous flow. Those that have protruding lines tend to grow moss, as well as collect dirt and debris over time.
Aluminum
Aluminum is the most commonly used material when it comes to greenhouse frames. The nice thing about it is it can be powder-coated in any color you like.
While it’s long-lasting, it can’t insulate heat efficiently. So, you’ll have to make up for that with the type of glazing you pick.
Timber
Timber greenhouses, usually cedar, provide an attractive addition to your garden. Wooden greenhouses are great at maintaining a constant temperature day and night.
They can also be glazed all the way to the ground or only half-way with the rest covered in bricks. While this may hold the heat within the greenhouse pretty well, it means you can grow plants at lower levels.
Plastic Resin
Plastic resin frames lack the sturdiness of metal or wooden frames. This makes them better suited for small greenhouses.
Yet, what they lack in durability, they make up for in attractiveness and affordability. They also retain heat pretty well.
Steel
Strong and long-lasting are two words that come to mind when we talk about galvanized steel frames. Since steel is known for its sturdiness, it’s capable of holding up to extreme weather conditions.
Another advantage is that this frame is tubular. This means less structuring material, which means less cost.
Flooring
The best floor setup is one that’s both level and firm. Experts recommend starting with a hard ground cover, followed by a layer of sand. Next, come layers of gravel of paving slabs.
These layers will make drainage easier and cleaning hassle-free. They also allow you to damp down the flooring to maintain humidity inside the greenhouse.
Glazing/Insulation
For greenhouse glazing, there are several options to choose from, from horticultural glass to fiberglass.
Pro-tip: before glazing, spread white gravel along the external base of your greenhouse. The white helps reflect light into the greenhouse to decrease shadows and increase light exposure.
Horticultural Glass
Horticultural glass is affordable and long-lasting. One of the great things about glass is it lets in the maximum amount of light. However, it doesn’t provide sufficient insulation.
Toughened Glass
Toughened glass has all the advantages of horticultural glass plus a few extras. For starters, it’s more durable and versatile than standard glass.
It’s also five times more heat and scratch-resistant. Yet, their best advantage is their enhanced safety properties. If they ever crack, they break into circular chunks rather than sharp, piercing shards.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass is one of the most durable and long-lasting glazing materials. It’s translucent and allows for plenty of light to enter the greenhouse. Plus, it’s better at retaining heat than glass.
Polyethylene Film
Polyethylene film is more popular with expansive greenhouses. It’s the least expensive and the easiest to put up.
Being translucent, it allows light to pass through. Moreover, it’s pretty good at preserving heat.
The main downside is that it’s susceptible to snags and tears. Polyethylene film also tends to sag in high winds or snow.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate doesn’t break and it’s easy to maintain year-round. Another advantage is that it provides a higher level of insulation.
Conversely, it doesn’t let in direct sunlight because it’s opaque. This can cause sun-loving plants to suffer. Plus, it may snap out of its frame during extremely high winds. To boost its life expectancy, make sure it’s UV-treated.
Polycarbonate coverings are available in three types:
- Thin-walled
- Triple-walled
- Twin-walled
Ventilation
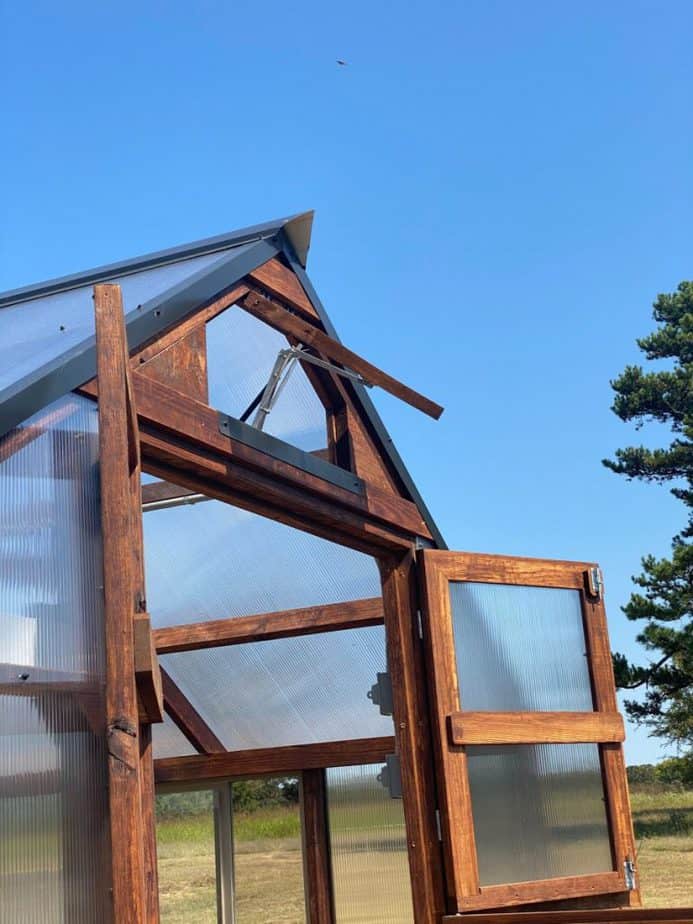

Ventilation is vital for a greenhouse to remain in good condition. This is doubly important during summer.
A typical greenhouse should have a couple of roof vents and some fans. There should also be one or two side vents, depending on the size of the unit. Some also have exhaust fans.
Pro-tip: installing an automatic vent is one of the best investments you can make. You can customize them to reduce energy and maintain an ideal environment.
Accessories
Here are a few fun and handy accessories you’ll need to spruce up your greenhouse.
Potting Benches
Potting benches are designed to help you grow your own seeds. They provide a durable surface work area where you can keep all your potting needs in one area.
Custom Shelving
Aluminum shelves are the most common and most versatile. They’re also easy to clean and maintain.
Best of all, they allow you to customize your greenhouse to create more space. You can also arrange them to create fun geometrical designs.
Heaters
There are multiple greenhouse heaters available on the market, such as:
- Grow lights: they provide heat for the plants, but not enough to reach the soil
- Toaster-coil or lamp heaters: designed to spot heat corners or small areas
- Track system heaters: installed in the ceiling to heat the whole greenhouse
Automatic Irrigation Systems
One of the most disheartening things that can happen to your plants is that you forget to water them. This is where automatic irrigation systems can help.
There are three main types of these systems. Each of them can be set on battery-operated timers that give your plants water at preset times.
These three systems are:
- Soaker hoses
- Drip-irrigation systems
- Drip tape
Hand-Watering Wands
This wand has a ‘fine misting’ setting. This is best used with delicate seedlings and sprouts. The wand can also help you reach seedling trays that are too high or too far back to reach.
Galvanized Steel Braces
If your greenhouse base needs reinforcement, these braces will do the job perfectly. They’re best used in areas with strong winds to prevent the greenhouse from shifting or tipping over.
Design

Greenhouse suppliers now offer the choice between two designs: freestanding or lean-to. Freestand greenhouses are more affordable and easier to install. They’re also better suited for seasonal use. Their only drawback is that supplying them with power and water can be costly.
On the other hand, lean-tos are greenhouses that are connected to your home. They allow you to grow plants year-round and provide easier access year-round, day or night. Their downside is that they tend to lack proper ventilation.
To Buy A Greenhouse Or Not, That Is The Question!

Greenhouses help maintain a stable and regulated indoor environment for your plants. Their functionality makes them perfect for growing almost any type of plant. The best part is it doesn’t matter where you live or what the weather is like.
If you’re getting to expand your gardening skills, use our guide on how to buy a greenhouse. This way, you can know exactly the right type of greenhouse that best serves your gardening needs for many years to come.




